English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик
How Is a Load Interrupter Switch Applied Across Medium-Voltage Power Distribution Networks?
2025-12-16
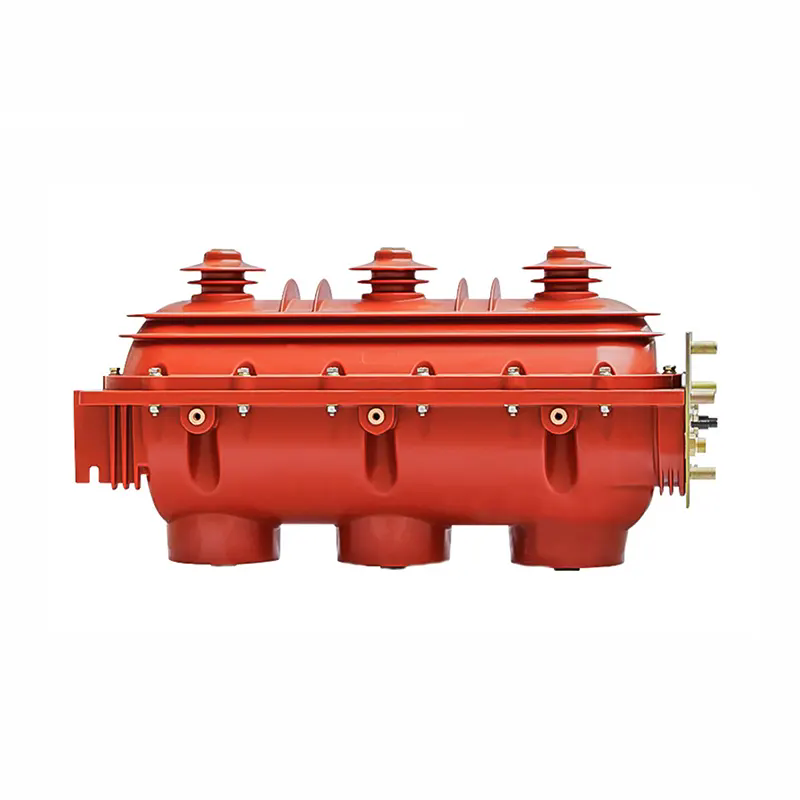
A Load Interrupter Switch (LIS) is a critical switching device used in medium-voltage power distribution systems to safely make or break load currents under normal operating conditions. It is commonly installed in substations, ring main units, industrial power systems, and utility distribution networks where controlled isolation and operational continuity are required. Unlike simple disconnectors, a Load Interrupter Switch is specifically engineered to interrupt current without causing damage to the system or creating unacceptable arc hazards.
The central purpose of this article is to explain how a Load Interrupter Switch operates within real-world power distribution environments, how its structural and electrical parameters influence performance, and how it aligns with evolving grid requirements. By examining design characteristics, application scenarios, and operational considerations, this content provides decision-makers, engineers, and procurement specialists with a clear technical reference aligned with common search behavior and professional reading habits.
Load Interrupter Switches are typically used for feeder control, sectionalizing, transformer isolation, and loop network management. They are often paired with fuses or protection relays to provide coordinated fault protection while maintaining system reliability. Their role becomes increasingly important as power systems expand, decentralize, and integrate renewable and distributed energy resources.
Technical Structure and Key Parameters
From a technical standpoint, a Load Interrupter Switch integrates mechanical switching components with arc-quenching technology, insulation systems, and manual or motorized operating mechanisms. The design allows the switch to interrupt rated load current while maintaining dielectric integrity before and after operation.
Below is a consolidated overview of typical technical parameters for a medium-voltage Load Interrupter Switch. Actual values may vary depending on system requirements and regional standards, but the parameters listed reflect common industry configurations.
| Parameter | Typical Specification Range |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 12 kV / 24 kV / 36 kV |
| Rated Current | 400 A / 630 A |
| Rated Short-Time Withstand Current | 16 kA – 25 kA (1–3 s) |
| Rated Making Capacity | Up to 63 kA peak |
| Insulation Medium | SF₆ gas / Vacuum / Air |
| Operating Mechanism | Manual / Motor-operated |
| Installation Type | Indoor / Outdoor |
| Mechanical Endurance | ≥ 5,000 operations |
| Applicable Standards | IEC 62271-103, IEC 62271-200 |
These parameters directly affect how the Load Interrupter Switch performs during routine switching operations, maintenance isolation, and network reconfiguration. For example, rated current and short-time withstand capability determine suitability for heavily loaded feeders, while insulation medium influences maintenance intervals and environmental compatibility.
Structurally, most Load Interrupter Switches are designed with visible isolation, ensuring a clear open gap for maintenance safety. This feature is particularly valued in utility and industrial environments where operational verification is mandatory. Additionally, interlocking systems are commonly integrated to prevent misoperation, such as closing the switch when grounding is engaged.
System Integration and Operational Considerations
When applied within a power distribution system, the Load Interrupter Switch serves as both an operational and safety device. Its primary role is not fault interruption at high short-circuit levels, but controlled switching under load and secure isolation during maintenance or system reconfiguration.
In ring main units and secondary substations, Load Interrupter Switches enable flexible network topology. Sections of the network can be isolated without disrupting upstream or downstream supply, supporting higher service continuity. In industrial facilities, they allow controlled shutdown of specific process lines or transformers while keeping the remainder of the system energized.
Coordination with protective devices is a key operational consideration. In many designs, a Load Interrupter Switch is combined with current-limiting fuses. During fault conditions, the fuse clears the fault, while the switch provides visible isolation and safe disconnection. This coordination reduces equipment stress and simplifies post-fault maintenance.
Environmental and installation factors also influence performance. Outdoor Load Interrupter Switches must withstand temperature variations, humidity, pollution, and UV exposure. Indoor variants, particularly in metal-enclosed switchgear, emphasize compactness and operator safety. The choice between gas-insulated, vacuum, or air-insulated designs often reflects regulatory trends, lifecycle cost analysis, and maintenance strategy rather than a single technical advantage.
Common Questions About Load Interrupter Switches
Q: How does a Load Interrupter Switch differ from a circuit breaker in practical applications?
A: A Load Interrupter Switch is designed to interrupt rated load current and provide isolation, whereas a circuit breaker is capable of interrupting high fault currents repeatedly. In practice, Load Interrupter Switches are used for operational switching and sectionalizing, while circuit breakers handle system protection. This distinction allows cost-effective system design without compromising safety or reliability.
Q: How is operational safety ensured during switching and maintenance?
A: Operational safety is achieved through visible isolation gaps, mechanical and electrical interlocks, grounding switches, and compliance with international standards. These features ensure that the switch cannot be operated under unsafe conditions and that maintenance personnel can visually confirm isolation before work begins.
Industry Direction, Application Expansion, and Brand Reference
As power distribution networks continue to evolve, the role of the Load Interrupter Switch is expanding in parallel. Urbanization, grid automation, and distributed energy integration are driving demand for equipment that supports flexible operation, compact installation, and high reliability. Utilities and industrial users increasingly expect switching devices to integrate seamlessly with monitoring systems, remote operation platforms, and standardized modular switchgear.
Manufacturers are responding by refining mechanical endurance, optimizing insulation systems, and aligning designs with stricter environmental and safety expectations. While the fundamental operating principle of the Load Interrupter Switch remains consistent, its application scope continues to broaden across renewable energy substations, data centers, transportation infrastructure, and smart grid projects.
In this context, DAYA provides Load Interrupter Switch solutions designed to meet international standards and diverse application requirements. Through structured engineering, controlled manufacturing processes, and application-focused configurations, DAYA supports customers seeking stable performance and long-term operational consistency in medium-voltage distribution systems.
For project consultation, technical clarification, or product selection support related to Load Interrupter Switch applications, interested parties are encouraged to contact us directly. A dedicated technical team is available to discuss system requirements, configuration options, and implementation considerations aligned with local standards and operational expectations.