 English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик
How Does a Dry-type Transformer Operate and What Are Its Key Specifications?
2025-12-26
Article Summary: This comprehensive article explores Dry-type Transformers, detailing how they operate, their specifications, common questions, and practical applications in various industries. It provides a structured guide for engineers, procurement specialists, and technical enthusiasts seeking in-depth knowledge of Dry-type Transformers.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Dry-type Transformers
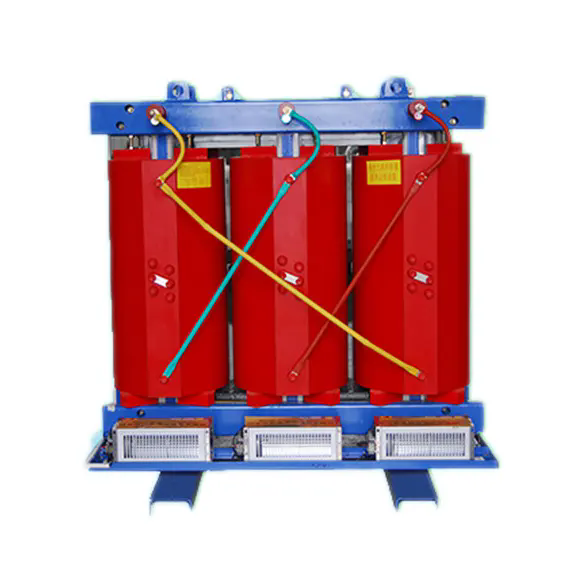
Dry-type transformers are electrical devices designed to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits without using liquid insulation, relying instead on air or solid insulation materials. They are widely used in industrial, commercial, and utility applications due to their safety, low maintenance, and environmental friendliness. The core purpose of this article is to provide a thorough understanding of Dry-type Transformers, focusing on operational principles, technical specifications, maintenance best practices, and industry-specific applications.
These transformers are designed to provide reliable voltage regulation while minimizing risks associated with flammable liquids. Key components include the laminated core, copper or aluminum windings, and high-quality insulation materials. By understanding the technical parameters and operational considerations, stakeholders can optimize transformer selection and ensure safe and efficient operation across a wide range of scenarios.
2. Technical Specifications and Parameters
Dry-type transformers come in multiple configurations with varying voltage ratings, capacities, and insulation classes. Below is a summary of typical specifications for high-performance dry-type transformers:
| Parameter | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Rated Power | Nominal capacity of the transformer in kVA or MVA | 10 kVA – 5000 kVA |
| Primary Voltage | Voltage applied to the primary winding | 380 V – 36 kV |
| Secondary Voltage | Voltage delivered by the secondary winding | 110 V – 36 kV |
| Insulation Class | Thermal classification of insulating materials | Class A (105°C) – Class H (180°C) |
| Cooling Method | Natural Air (AN) or Forced Air (AF) | AN, AF |
| Frequency | Nominal operating frequency | 50 Hz / 60 Hz |
| Impedance | Percentage of voltage drop under full load | 4% – 8% |
| Efficiency | Energy conversion efficiency under full load | 95% – 99% |
These specifications ensure that engineers and facility managers can assess compatibility with existing systems, evaluate performance requirements, and predict long-term operational efficiency.
3. Common Questions About Dry-type Transformers
Q1: How does a dry-type transformer differ from an oil-immersed transformer?
A1: Dry-type transformers use air or solid insulation instead of oil, which reduces fire risk, maintenance requirements, and environmental hazards. While oil-immersed transformers have higher cooling efficiency, dry-type transformers are ideal for indoor or sensitive applications due to their non-flammable nature.
Q2: How can the lifespan of a dry-type transformer be maximized?
A2: Proper installation, regular thermal monitoring, and adherence to load limits are critical. Overheating is the primary cause of insulation degradation. Implementing preventive maintenance, avoiding moisture exposure, and using compatible cooling methods ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Q3: How are dry-type transformers rated for power and voltage?
A3: Dry-type transformers are rated based on their nominal power capacity (kVA/MVA) and voltage levels on both primary and secondary windings. Ratings are standardized according to IEC and IEEE standards, which ensure uniform performance, compatibility, and safety across diverse applications.
4. Applications, Maintenance, and Industry Trends
Dry-type transformers are extensively used in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and utility networks. Common applications include:
- Industrial machinery power distribution
- Data centers and critical infrastructure
- Hospitals and educational institutions
- Renewable energy systems, including solar and wind integration
Maintenance practices for dry-type transformers emphasize cleanliness, thermal monitoring, and electrical testing. Infrared thermography can identify hot spots, while regular electrical insulation tests detect early degradation. These measures reduce downtime and prevent costly failures.
Industry trends indicate growing adoption of environmentally friendly, high-efficiency dry-type transformers. The focus is on compact designs, improved thermal performance, and compliance with international energy efficiency standards. Advanced materials and intelligent monitoring systems further enhance operational reliability and safety.
5. DAYA Electrical Solutions and Contact
DAYA Electrical provides a comprehensive range of Dry-type Transformers designed for high performance, safety, and energy efficiency. Their solutions cater to industrial, commercial, and utility clients, ensuring seamless integration with existing electrical infrastructure. The expertise of DAYA Electrical ensures optimal transformer selection, installation support, and ongoing maintenance consultation.
For detailed inquiries or to request a quotation, please contact us and our team will provide professional guidance and customized solutions to meet your project requirements.




